Purpose of Deoxidation of Steel
The fundamental purpose of steel deoxidation is to remove excess oxygen elements in the molten steel to ensure the quality of the steel. Oxygen atoms are distributed between iron atoms, and there is a certain attraction between oxygen atoms and iron atoms. It is generally believed that it is dissolved in metal with FeO. The experiment found that the temperature is in the range of 1519-1700 degrees Celsius, and the solubility of oxygen in iron is close to a linear relationship with the temperature, and increases with the temperature.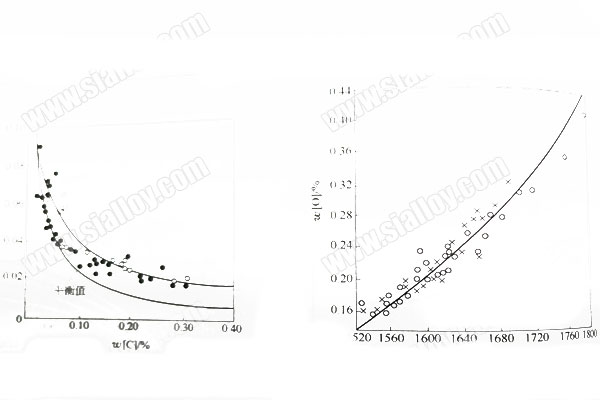
In the steelmaking process, the molten steel is not in contact with pure FeO slag, and the oxygen dissolution process has not reached equilibrium, so the actual oxygen content in the molten steel is always lower than the calculated value at the same temperature. The study found that the actual oxygen content of the molten steel mainly depends on the carbon content of the molten steel, followed by the FeO content and temperature in the slag.
The basic task of deoxidation mainly includes three aspects: First, according to the requirements of different steel grades to remove excess oxygen. The primary task of deoxidation is to remove excess oxygen according to the steel grade. According to the different levels of deoxidation, steel can be divided into three types of killed steel, boiling steel and semi-killed steel; second, the deoxidation products are excluded, and the deoxidation operation must ensure that the deoxidation products in the molten steel are excluded to the maximum extent, otherwise, the steel The total amount of oxygen has not decreased, but the FeO in the molten steel is replaced with another oxide, or just the dissolved oxygen in the steel is converted into oxygen in the compound state. In actual production, compounding is often used Measures such as deoxidation, adjustment of the order of addition of ferro silicon, silicon manganese and other alloys, and enhancement of agitation can promote deoxidation of the deoxidized substance. Third, adjust the composition of molten steel. When deoxidizing the molten steel, a part of the deoxidizing agent fails to participate in the deoxidizing reaction and remains and dissolves in the molten steel. Therefore, in the production of carbon steel, especially according to the recovery rate of alloy elements, the content of silicon and manganese in the molten steel is adjusted while deoxidizing by controlling the amount of alloy addition.
 中文
中文




